Portfolio management sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the intricacies of managing portfolios, we uncover the key components that drive success in the world of investments.
From understanding the concept of portfolio management to exploring the importance of diversification and risk management, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of investment strategies with confidence.
Definition of Portfolio Management
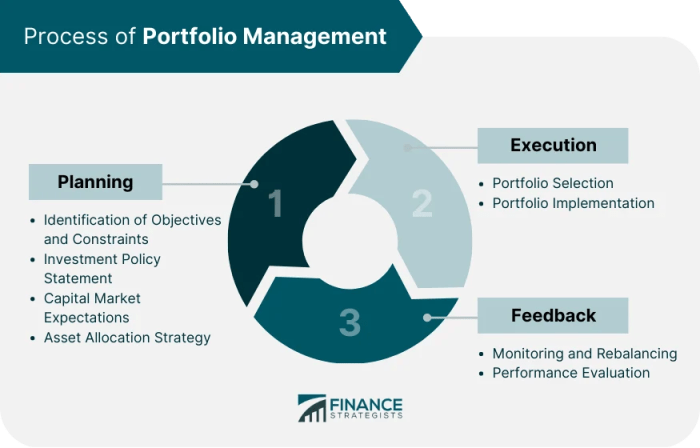
Portfolio management refers to the process of managing a group of investments owned by an individual or an organization. It involves making decisions about what assets to include in the portfolio, how to allocate resources among different assets, and how to monitor and adjust the portfolio over time to achieve specific financial goals.
Main Objectives of Portfolio Management
- Diversification: The primary objective of portfolio management is to spread investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
- Risk Management: Portfolio managers aim to minimize risk while maximizing returns based on the investor's risk tolerance.
- Return Maximization: Another key objective is to generate the highest possible return on investment within the risk parameters set by the investor.
Types of Portfolios
- Equity Portfolio: Consists of stocks or shares of companies, providing ownership in the form of equity.
- Fixed-Income Portfolio: Comprised of bonds and other fixed-income securities that pay a regular interest income.
- Mutual Fund Portfolio: A collection of mutual funds managed by professionals, offering diversification and professional management.
Importance of Portfolio Diversification
Diversifying a portfolio is a crucial strategy in managing investments effectively. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and regions, investors can reduce risk and improve potential returns.
Benefits of Diversified Portfolio
- Diversification helps mitigate risk: When one asset underperforms, others may offset the losses, reducing overall portfolio volatility.
- Potential for higher returns: A well-diversified portfolio can capture growth opportunities in various sectors, maximizing potential profits.
- Enhanced stability: Diversification can provide a more stable and consistent performance over time, especially during market fluctuations.
Strategies for Effective Portfolio Diversification
- Asset Allocation: Allocate investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities to balance risk and return.
- Diversification within Asset Classes: Spread investments within each asset class to further reduce risk, such as investing in different industries or geographic regions.
- Rebalancing: Regularly review and adjust portfolio allocations to maintain the desired level of diversification based on financial goals and market conditions.
- Consider Correlations: Select assets with low correlations to each other to achieve true diversification and minimize the impact of market movements.
Risk Management in Portfolio
Risk management plays a crucial role in portfolio management by helping investors minimize potential losses and maximize returns. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, investors can protect their investments and achieve their financial goals more effectively.
Types of Risks in Portfolio Management
- Market Risk: This type of risk arises from factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and market volatility.
- Credit Risk: Credit risk is associated with the potential for a borrower or issuer to default on their financial obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: Liquidity risk refers to the possibility of not being able to buy or sell an investment quickly at a fair price.
- Reinvestment Risk: Reinvestment risk occurs when cash flows from an investment cannot be reinvested at the same rate of return.
Risk Mitigation Techniques in Portfolio Management
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors can help reduce overall risk exposure.
- Asset Allocation: By strategically allocating assets based on risk tolerance and investment goals, investors can manage risks effectively.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting predetermined price levels to automatically sell an investment can limit potential losses.
- Hedging: Using derivatives or other financial instruments to offset potential losses in a portfolio.
Portfolio Performance Evaluation
When it comes to managing a portfolio, evaluating its performance is crucial to determine its success and make informed decisions for future investments. By analyzing various key performance indicators and assessing the portfolio's performance over time, investors can gauge the effectiveness of their investment strategy.
Key Performance Indicators
- Return on Investment (ROI): This indicator measures the profitability of the portfolio by comparing the gains or losses against the initial investment.
- Sharpe Ratio: A measure of risk-adjusted return, the Sharpe ratio helps investors understand how much return they are receiving for the level of risk taken.
- Alpha: Alpha measures the excess return of the portfolio compared to its benchmark index, indicating the manager's skill in generating returns.
- Standard Deviation: This metric assesses the volatility or risk associated with the portfolio, helping investors understand the potential fluctuations in returns.
Analyzing Portfolio Performance Over Time
One method for analyzing the performance of a portfolio over time is to calculate the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), which provides a smooth representation of the portfolio's growth over a specified period. Tracking the CAGR helps investors understand the consistent annual growth rate of their investments.
Additionally, comparing the portfolio's performance against relevant benchmarks or indices can provide valuable insights into how well the portfolio is performing relative to the market. This benchmarking helps investors assess whether their portfolio is outperforming or underperforming the broader market trends.
Asset Allocation Strategies

Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of portfolio management that involves dividing investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, cash, and real estate. By strategically allocating assets, investors can manage risk and optimize returns based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves setting target allocations for various asset classes based on long-term investment objectives and risk tolerance. This strategy aims to maintain a well-diversified portfolio that aligns with the investor's financial goals over an extended period.
- Determine long-term financial goals and risk tolerance
- Select target allocation percentages for different asset classes
- Rebalance the portfolio periodically to maintain target allocations
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation focuses on short to medium-term opportunities by adjusting asset allocations based on market conditions and economic outlook. This strategy allows investors to capitalize on short-term trends and market inefficiencies.
- Monitor market conditions and economic indicators
- Adjust asset allocations based on short-term opportunities
- Reallocate assets as market conditions change
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation involves dynamically adjusting asset allocations based on market conditions, economic trends, and investment opportunities. This strategy allows for more flexibility in responding to changing market dynamics and optimizing portfolio performance.
- Utilize quantitative models and market analysis
- Implement active management strategies to capitalize on market trends
- Regularly review and adjust asset allocations based on performance
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, portfolio management is a dynamic field that requires a delicate balance of strategy, risk assessment, and performance evaluation. By mastering the art of asset allocation and diversification, investors can unlock the full potential of their portfolios and achieve their financial goals with precision.
FAQs
What are the main objectives of portfolio management?
The main objectives of portfolio management include maximizing returns, minimizing risks, and achieving investment goals within a specified time frame.
How is portfolio performance evaluated?
Portfolio performance is evaluated through key performance indicators such as return on investment, risk-adjusted returns, and portfolio volatility.
What are some strategies for effective portfolio diversification?
Strategies for effective portfolio diversification include spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall risk exposure.
Why is asset allocation important in portfolio management?
Asset allocation is crucial in achieving investment goals as it helps in balancing risk and return by determining the optimal mix of assets based on an investor's risk tolerance and financial objectives.











